
National Grid’s Future Energy Scenarios (FES) 2024 have released a detailed urgent pathway to achieving net zero by 2050 targets. Jaspreet Singh, Associate Sustainability Consultant at Tetra Tech, breaks down the key points of the report for various private and public stakeholders.
On July 15, 2024, National Grid unveiled its highly anticipated FES 2024, alongside a series of insightful seminars. The FES are comprehensive pathways that project various routes to achieving net zero by 2050. These pathways explore how different policy decisions, energy production penetration deployments, technological advancements, and societal behaviours could shape the future of energy systems. By providing these insights, FES serves as a crucial resource for industrial and policy stakeholders.
The core message of this year’s FES 2024 report is clear:
“Decisive action is needed within the next two years to deliver the fundamental change required for a fair, affordable, sustainable, and secure net zero energy system by 2050.”
FES 2024 highlights the critical urgency for decarbonisation across all sectors. Here are some key insights from FES 2024:
- Pathways and not Scenarios to Net Zero: FES 2024 pivots from the broad range of scenarios seen in previous editions to a more focused and plausible set of pathways, all uniformly targeting the 2050 net zero goal (along with a counterfactual). This is a shift from FES 2023 where the scenarios were relatively broad with one of the scenarios – ‘leading the way’ targeting net zero by 2046. The FES 2023 scenarios and FES 2024 pathways are presented in the illustration below.
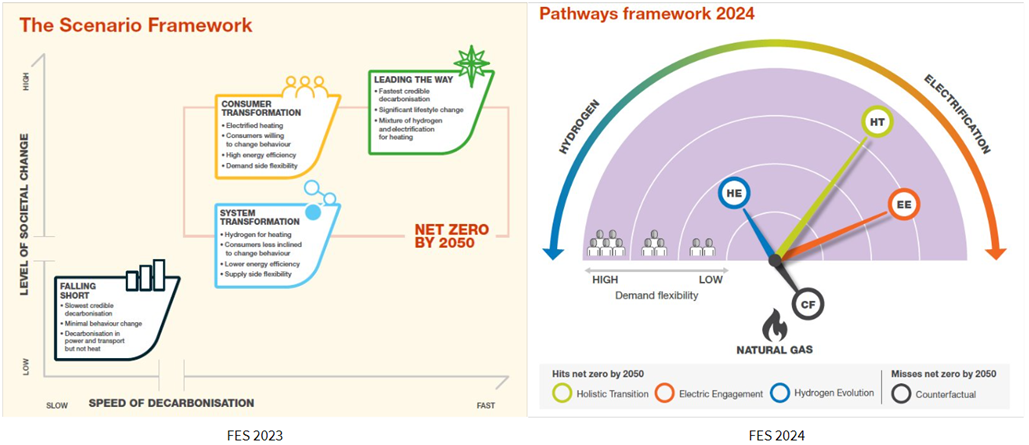
Source: FES 2024 National Grid ESO
- Electrification’s Central Role: Electrification emerges as a central theme in the FES 2024. The FES predicts that electricity will achieve average annual negative emissions by 2050, measured in terms of kgCO2e per kWh in all net zero pathways. It’s evident that electrification of demand, including vehicles and heating, is not just likely but inevitable. Furthermore, in the hydrogen evolution pathway, hydrogen helps meet about 30% of overall energy demand, with the remaining demand met by electricity, underscoring the critical role of electrification in decarbonisation.
- Uniform EV Adoption Rates: One of the most significant updates in the Future Energy Scenarios (FES) 2024 is the alignment of net zero electric vehicle (EV) adoption rates with the Zero Emissions Vehicle (ZEV) mandate. This mandate sets ambitious targets, requiring 80% of new cars and 70% of new vans sold in Great Britain to be zero emission by 2030, increasing to 100% by 2035. This alignment ensures a unified approach towards full electrification of cars and vans, providing a clear timeline for the transition. It offers both manufacturers and consumers the certainty needed to embrace electric mobility.
- Increased Insulation Contribution: Demand-side reduction enabled by insulation is poised to play a more critical role than previously anticipated. FES 2024 highlights that all net zero pathways now anticipate higher levels of energy savings from insulation at homes, a departure from FES 2023. In the previous year’s scenarios, the system transformation scenario showed insulation to have a lower impact on energy demand levels compared to the current pathways. This change highlights the importance of energy efficiency in achieving net zero goals.
- Hydrogen Utilisation: Directives from UK authorities are expected to be pivotal, particularly the forthcoming decision in 2026 regarding the role of hydrogen in heating systems, which may hold significant influence. The current ‘Hydrogen Evolution’ pathway within the FES 2024 outlines a vision for hydrogen as a central heating medium, with goals to establish a comprehensive network by 2050, starting with industrial clusters by 2030. In contrast, the ‘Holistic Transition’ approach suggests a more conservative strategy, limiting hydrogen heating largely to industrial zones.
- Increased Demand Flexibility: Smart grids and smart demand-side management are becoming increasingly crucial for efficiently balancing energy supply and demand. Emerging technologies like vehicle-to-grid (V2G), which enable electric vehicles to return power to the grid when needed, are anticipated to play a more significant role than previously expected. For instance, according to FES 2024, National Grid projects that V2G will provide c. 60% more peak capacity flexibility than what was predicted in the FES 2023 analysis.
- Methane Reformation and CCS: Methane reformation is a method for producing hydrogen by reacting methane with steam at high temperatures in the presence of a catalyst. This method also produces carbon emissions. The report highlights that methane reformation combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS) will be crucial for achieving the decarbonisation goals outlined in the Sixth Carbon Budget.
- Higher importance on BECCS: Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) levels have grown in all net zero pathways. Electric Engagement and Hydrogen Evolution scenarios project BECCS capacity reaching around 4.5 GW by 2050, up from zero currently.
- Growing Importance of DACCS: Direct Air Capture with Carbon Storage (DACCS) is now featured in all pathways, reflecting its emerging importance in our decarbonisation strategy, despite being a relatively new technology.
- Long-term dependence on Nuclear Power: The reliance on nuclear energy is expected to increase compared to FES 2023, following the release of the “Civil Nuclear: Roadmap to 2050,” which outlines the UK government’s vision for nuclear power. Projections estimate nuclear capacity to grow to between 11-22 GW by 2050, up from the current c.6 GW. This expansion comes after a brief anticipated decline in capacity from 2026 to 2030, as National Grid expects most existing nuclear power stations to retire by 2030.
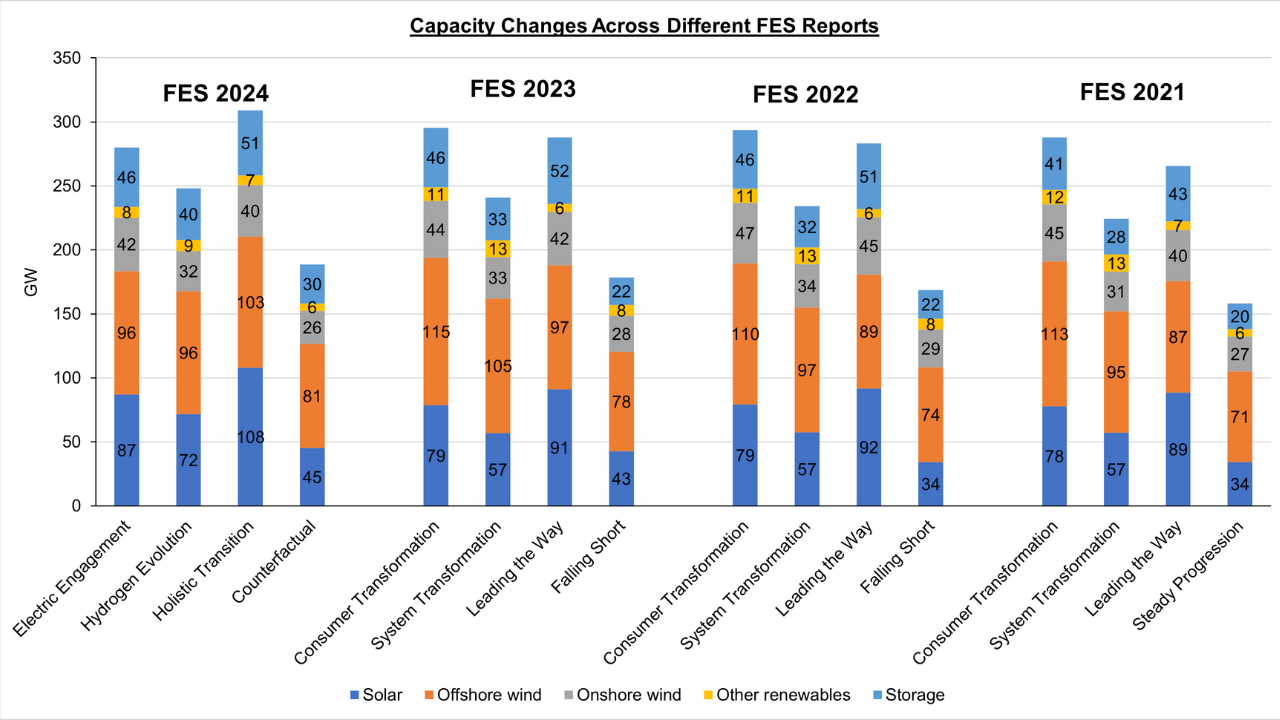
- Renewable Energy and Storage Capacities: Notably, the capacity predictions for renewable energy and storage have evolved. Above is a comparison of offshore wind, onshore wind, other renewables, and storage capacities across FES 2021 to FES 2024. It’s evident that solar PV is playing a significantly larger role than previously anticipated, while the National Grid has refined projections for other renewables and adjusted adoption rates to more realistic and practical levels.
In conclusion, FES 2024 presents a clear, urgent call to action. The strategic pathways outlined necessitate immediate and decisive action to achieve the net zero target by 2050. At Tetra Tech, we are ready to align our efforts with these insights and support you in contributing effectively to this critical transition. Let’s continue to work together to green the grid, utilise electrification, improve energy demand by retrofitting buildings, transition to zero emission vehicles and implement smart systems.
Connect with us. Reach out to our experts.